Accessibility and Compliance Best Practices for Your Site
In today’s inclusive digital landscape, ensuring that your website is both accessible and compliant is no longer optional. A site that’s easy to use for people of all abilities not only protects you legally, but it enhances SEO, usability, and brand reputation as well.
Let’s break down what accessibility and compliance mean, how to make your site friendly for everyone, and how to steer clear of legal pitfalls.
What Are The Accessibility Requirements For My Site?
Accessibility means designing and building your site so people with disabilities can navigate and interact with it in a meaningful way. ADA, WCAG, and Section 508 have set the legal and technical standards for accessible websites covering many US-based sites and institutions. Ever since these standards have been set, lawsuits continue to rise. Even small businesses have faced threats for inaccessible content - sometimes over PDFs or basic layout issues. This can be costly and burdensome as well as frustrating. Proactive, inclusive design is the best prevention. This is not just a smart tactic, but it also shows that your business cares about accessibility inclusion, setting you apart ethically and commercially.
Site Accessibility Checklist
Here’s your action checklist for making your site inclusive:
Structure content semantically: Use correct headers, lists, and landmarks so assistive technologies, like screen readers, can guide users properly
Write helpful alt text: Every meaningful image needs a clear, concise description. As an added bonus, this boosts image SEO as well
Improve visual accessibility: Ensure color contrasts meet WCAG standards, and confirm your site works without a mouse
Validate interactive element labels: Buttons must have readable text or labels. Use valid ARIA roles and attributes where needed
Test, test, test: Use tools like Lighthouse (see screenshot of how to access), WAVE, or W3C validators to flag issues early. Regular audits catch regressions and support your accessibility roadmap. W3C also provides a list of tools to help you perform audits
What Are The Compliance Considerations For My Site?
When you launch a website, it’s easy to focus on design, branding, and content, but one area many site owners overlook or just don’t think about is legal compliance. Whether you’re running a small blog, a growing e-commerce store, or a service-based business, certain policy pages aren’t just “nice to have,” but rather, they are legally required in many regions.
Overview of Legal Policy Pages
These policy pages exist to protect both you and your visitors. They build trust, keep you compliant with regional laws, and can even shield you from costly legal disputes. The exact pages you need depend on your location, audience, and business model. Most websites need a baseline set including a Privacy Policy, Terms & Conditions, Accessibility Policy (see above), and a Cookie Policy. From there, you can add industry-specific policies as needed. We always recommend talking to your legal advisors to ensure you are in good standing, but use this as an overview of what to ask for.
Privacy Policy: Nearly every modern privacy law, from Europe’s GDPR to California’s CCPA/CPRA, requires you to tell visitors what personal information you collect (such as email addresses, IPs, cookies, or payment details), how you use it, and who you share it with. If your site uses forms, analytics, or payment processing, a Privacy Policy is mandatory.
Terms & Conditions (or Terms of Service): This isn’t legally required everywhere, but it can be valuable because it protects you by setting rules for how people can use your site. It’s especially important if you sell products, offer memberships, or publish original content that you want to protect.
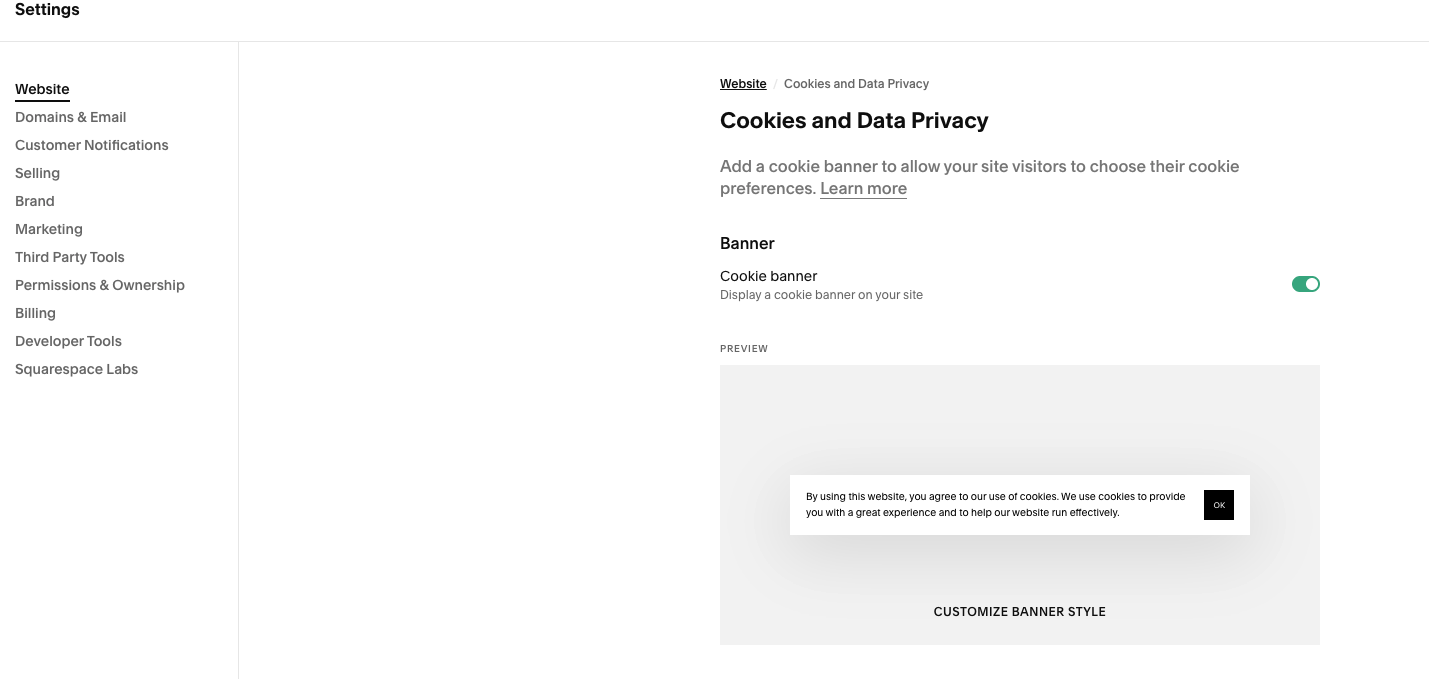
Cookie Policy + Cookie Consent Banner: Cookie policies are required if you serve visitors in the EU or UK or if your site uses tracking technologies like Google Analytics or advertising pixels (we definitely recommend Google Analytics). These are required by the GDPR and ePrivacy Directive, and they give users control over whether their data is being tracked. Keep in mind - Squarespace does provide a Cookie Consent Banner within the settings that you can utilize.
Refund, Return, and Shipping Policies: These policies are often legally mandated under consumer protection laws for e-commerce businesses.
Disclaimers: Certain industries (like health, finance, or law) benefit from this policy to clarify that your content is informational and not professional advice.
Accessibility Statement: As mentioned above, digital accessibility laws have expanded, making an accessibility statement both a legal safeguard as well as a mark of inclusivity.
If you are unsure of where to start or you do not have legal counsel, we recommend (and use) Termageddon as a paid resource (use code holisticm for a 10% discount) that will help you determine what policies are most appropriate for your site and draft language for you. If you decide to use Termageddon, reach out to us and we will get you set up with free training!
TL;DR
It is no longer as simple as creating a website; you must meet accessibility and legal compliance standards. When you ensure everyone can experience your site as seamlessly as possible, you’re not only reducing legal risk, you’re also widening your audience, improving SEO, and delivering better user experiences across the board.